Nanobiotech 2019
About Conference
Theme: Challenges and Innovations in Next Generation Nanoscience
EuroSciCon Ltd is back with its 2nd Edition of Nanotech & Nanobiotechnology 2019 and this time it focuses around the advancements in the strategies and researches that are going ahead in the field of Nanoscience.
The Nanobiotech 2019 aims to bring together leading academic scientists, researchers and research scholars to exchange and share their experiences and research results about all aspects of Nanotechnology. It also provides the premier interdisciplinary forum for researchers, practitioners and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns, practical challenges encountered, and the solutions adopted in the field of Nanobiotechnology.
What’s New?
Nanotech and Nanobiotechnology 2019 includes international attendee workshops, lectures and symposia, including a designated registration area, a refreshment break and gala lunch. Nanotechnology educators can join the EuroSciCon as an international member to receive discounts on registration. The core aim of Nanotech and Nanobiotechnology 2019 conference is to provide an opportunity for the delegates to meet, interact and exchange new ideas in the various areas of Nanoscience. We invite students to attend the conference and gain more knowledge about nano science and technology from eminent researchers of the world. So, come and join leading experts and allied professionals from August 26-27, 2019 in Melbourne, Australia to discuss the ways to develop better technologies that will aid in the development of Nanotech and Nanobiotechnology.
Opportunities for Conference Attendees
For Researchers &Faculty:
Speaker Presentations
Poster Display
Symposium hosting
Workshop organizing
For Universities, Associations & Societies:
Association Partnering
Collaboration proposals
Academic Partnering
Group Participation
For Students & Research Scholars:
Poster Competition (Winner will get Best Poster Award)
Young Researcher Forum (YRF Award to the best presenter)
Student Attendee
Group Registrations
For Business Delegates:
Speaker Presentations
Symposium hosting
Book Launch event
Networking opportunities
Audience participation
For Companies:
Exhibitor and Vendor Booths
Sponsorships opportunities
Product launch
Workshop organizing
Scientific Partnering
Marketing and Networking with clients
Past Conference Report
EuroSciCon Conference on Nanotech and Nanobiotechnology 2018 was held on July 12- 13, 2018 in Paris, France. Researchers and students who attended from different parts of the world made the conference one of the most successful and productive events in 2018 from EuroSciCon Ltd. The Conference provided a platform for the Speakers from all over the world to share their research work on Nanotechnology. The two-day program witnessed thought provoking keynote and plenary presentations from experts in the field of Nanotechnology highlighting the theme, "Challenges and Innovation in Next Generation Nanoscience"
Sessions of Day 1 & Day 2 included
Day 1: (Chaired by Andreas Seifert & Co-chaired by Jinrich Kopecek)
Nanobiotechnology | NanoMedicine | Nanopharmaceuticals | Nano-Chemistry | Nanodevices and Nanosensors | Advancement in Nanotechnology
Day 2: (Chaired by Chantal Pichon & Co-chaired by Stephen D. Miller)
NanoMaterials | NanoRobotics | NanoElectronics | Cellular and subcellular Nanotechnology | Major Challenges in Nanobiotechnology
And our Key Note Speakers, which added the best to the part of our Program. Our Key Note Speakers were,
Julia Y. Ljubimova, USA
Tamara Minko, USA
Andreas Seifert, Spain
Chantal Pichon, France
Stephen D. Miller, USA
And our moderators, who did their best, to go everything so smoothly at the Conference, Thanks to Seyed Mohammad Mahdi Dadfar, Germany, who moderated for the first day of the conference, and Abraham J. Domb, Israel who moderated for the second day!!

Our heartiest thanks to all our participants, without whom this meeting would be impossible and won’t achieve this success. With the valuable feedback and generous response received from the participants of the event, EuroSciCon Ltd would like to announce the commencement of "2nd EuroSciCon Conference on Nanotech and Nanobiotechnology 2019" on August 26-27, 2019 at Melbourne, Australia.
Join us at Nanotech and Nanobiotechnology 2019!
Sessions & Tracks
Track 1: Nanotechnology
A standout amongst the most intriguing things about nanotechnology is that the properties of numerous materials change when the size of their measurements approaches nanometers. Nanotechnology is the examination of unique phenomenon and utilization of structures between 1 nanometer (nm) and 100 nanometers in size to enable novel applications. Products based on nanotechnology are as of now being used. Incorporating nanoscale science, designing, and innovation, nanotechnology includes imaging, estimating, demonstrating, and controlling matter at nano scale.
- Nanotechnology in materials science
- Nanotechnology in medicine
- Nanotechnology in agriculture
- Nanotechnology in food and packaging
- Nanotechnology in water treatment
- Green nanotechnology
- Environment, human health and safety issues of nanotechnology

Track 2: Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials are generally thought to be materials with no less than one outer measurement that measures 100 nanometers or less or with inner structures estimating 100 nm or less. They may be in the form of particles, rods, tubes or fibres. The nanomaterials that have an indistinguishable arrangement from known materials in mass shape may have diverse physico-synthetic properties than similar materials in mass frame and may carry on in an unexpected way. Nanomaterials have an extensive variety of uses ranging from medical devices to electronics, sustainable power technology, ecological remediation’s, healthcare, chemical industries and in different consumer items. Recent application of nanomaterials incorporates a scope of biomedical applications, for example, tissue engineering, drug delivery, and biosensors. Our session depicts a wide range of applications of nanotechnology and nanomaterials.
- Nanoparticles & nano powders
- Quantum dots
- Nanospheres & porous nanomaterials
- Nanorods and nanotubes
- Nanomaterials in chemical industry
- Nanomaterials applications
- Toxicity of nanomaterials
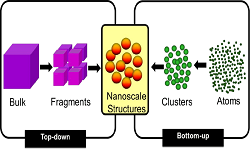
Track 3: Synthesis and Characterisation of Nanomaterials
The objective of any engineered technique for preparation of nanoparticles is to fabricate nanomaterials which have the unique properties for applications that are a result of their characteristic length scale being in the nanometer run (1 – 100 nm). Likewise, the manufactured strategy should show control of size in this range with the goal that one or the other property can be attained. There are two general strategies for synthesis of nanomaterials and the fabrication of nanostructures: “Bottom Up” and “Top Down”.
Bottom up approach refers to the build-up of a material from the bottom: start with atoms or molecules and build up to nanostructures. The starting material is either gaseous state or liquid state of matter for bottom up method.
Top down approach refers to cutting of a bulk material to get nano sized particle: begin with a pattern generated on a larger scale, then reduced to nanoscale. The starting material is in solid state for top down method.
- Photolithography
- Electron-beam lithography
- Nanosphere lithography
- Physical vapor deposition
- Chemical vapor deposition
- Micro-emulsion method
- Sol-gel method
- Spray Pyrolysis
- Molecular self-assembly
- Electrodeposition
Track 4: Nanodevices and Nanosensors
The Nanodevices and Nanostructures have presented a super trade of humankind with its Nano lifestyle machines. Nano scale materials are an extensively characterized set of substances that have no less than one basic measurement under 100 nanometers and have one of a kind electrical, magnetic, or optical properties. Ultrafine particulate matter is an outstanding case of nanoscale particles found in the earth. Nanodevices will finally have a huge impact on our capacity to enhance food production, improve human health, energy conversion and control pollution.
Nanosensors convey data about nanoparticles. Numerous logical achievements in Nanotechnology has been contributed by Nanosensors. Diverse kinds of sensors are developed from nanomaterials to distinguish a scope of substance vapors, to detect microbes or infections, to recognize single atoms to help pharmaceutical organizations in the generation of medications.
- Nanomedical devices
- Nanoswitches
- Magnetic nano devices
- Optical Nano sensors
- Nano-biosensors
- Latest research & applications of nanosensing
Track 5: Nanoelectronics and Nanophotonics
Nanoelectronics depend on the use of nanotechnology in the field of hardware and electronic segments. Despite the fact that the term Nanoelectronics may generally mean all the electronic parts, extraordinary consideration is given on account of transistors. These transistors have a size lesser than 100 nanometers. Obviously, they are little that different investigations must be made for knowing the quantum mechanical properties and between nuclear outline. Subsequently, however the transistors show up in the nanometer run, they are outlined through nanotechnology.
Nanophotonics is the investigation of the conduct of light on the nanometer scale, and of the association of nanometers-scale objects with light. It is a branch of optics, Nanotechnology, electrical building, and optical building. Nanophotonics is viewed as a pivotal innovation which is required to assume a corresponding part to small scale/nano hardware on chip and broaden the limit of media transmission systems.
- Nano transistors and nanowires
- Nanoelectronic devices
- Nano material electronics
- Optical properties of nanostructures
- Photonic & plasmonic nanomaterials
- Quantum nano-optics

Track 6: Carbon nanomaterials, devices and technologies
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are allotropes of carbon with a tube-shaped nanostructure. These hollow and cylindrical carbon nanotubes have strange properties, which are significant for electronics, optics, nanotechnology and different fields of materials science and technology. Nano carbon materials, for example, Graphene, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and fullerenes procure unprecedented properties. Carbon nanomaterials propose their utility as high portability electronic materials. Besides, the capacity to tune the band hole of semiconducting CNTs by means of control of distance across gives exceptional chances to redoing optical and optoelectronic properties. The properties of nanocarbons are extraordinarily reliant upon their synthesis.
- Carbon nanotubes (CNTs)
- Synthesis of carbon nanotubes
- Types of carbon nanotubes and related structures
- Characteristics of carbon-based nanomaterials
- Functionalization and applications of carbon nanotubes
Track 7: Graphene nanostructures
Graphene is a nuclear scale honeycomb cross section made of carbon particles. Graphene can be defined as a single, thin layer of graphite and known as a “super material”. Graphene has put researchers all over the world into work to understand it in a better way. Graphene is without a doubt rising as a standout amongst the most encouraging nanomaterials on account of its one of a kind blend of brilliant properties, which opens a route for its exploitation in a wide range of uses extending from electrical to optics, sensors, and biodevices.
- Graphene based nanomaterials
- Graphene Synthesis
- Chemistry and biology studies of graphene
- Applications of graphene in energy
- Applications of graphene in medicine

Track 8: Nanocomposites
Nanocomposite is a multiphase solid material where one of the phases has one, two or three dimensions of less than 100 nanometers (nm), or structures having nano-scale repeat distances between the different phases that make up the material. Nanocomposites are materials that consolidate nanosized particles into a matrix of standard material. The aftereffect of the expansion of nanoparticles is an exceptional change in properties that can incorporate mechanical quality, strength and electrical or warm conductivity. The adequacy of the nanoparticles is with the end goal that the measure of material included is typically just in the vicinity of 0.5 and 5% by weight. Nanoparticles have an amazingly high surface to volume proportion which significantly changes their properties when contrasted and their bulk measured counterparts. It additionally changes the manner by which the nanoparticles bond with the bulk material. The outcome is that the composite can be commonly enhanced as for the segment parts. Some nanocomposite materials have been appeared to be 1000 times harder than the bulk materials.
- Ceramic-matrix nanocomposites
- Metal-matrix nanocomposites
- Polymer-matrix nanocomposites
- Magnetic nanocomposites
Track 9: Advanced nanomaterials and nanoparticles
Nanomaterials are described as materials with no short of what one outside estimation in the size degree from around 1-100 nanometers. Nanoparticles are things with every one of the three outside estimations at the nano-scale. Built nanoparticles are deliberately delivered and arranged with specific properties related to shape, estimate, surface properties and science. These properties are reflected in fog concentrates, colloids, or powders. Routinely, the direct of nanomaterials may depend more on surface district than atom plan itself. The control of organization, size, shape, and morphology of nanomaterials and nanoparticles is a basic establishment for the improvement and use of Nano scale gadgets in everywhere throughout the world.
Nanoparticles can be built with unmistakable pieces, sizes, shapes, and surface sciences to empower novel procedures in an extensive variety of natural applications. The one of a kind property of nanoparticles and their conduct in organic milieu likewise empower energizing and integrative ways to deal with concentrate essential natural inquiries.
- Engineered nanomaterials & Biological interactions
- Polymer Nanotechnology
- Inorganic/Organic Nanomaterials
- Nanostructured Coatings, Surfaces and Membranes
- Emerging Multifunctional Nanomaterials for Solar Energy Extraction
- Toxicity of Nanoparticles

Track 10: Nanorobotics
A nanorobotics is a machine that can build and manipulate things precisely at an atomic level. Nanorobotics is the innovation of making machines or robots at or near the tiny size of a nanometre. Nanorobots would regularly be gadgets running in measure from 0.1-10 micrometers. The fundamental component utilized will be carbon as precious stone/fullerene nanocomposites in view of the quality and compound idleness of these structures. The other indispensable utilization of Nanotechnology in connection to medicinal research and diagnostics are nanorobots. Nanorobots, working in the human body, could screen levels of various mixes and record the data in their interior memory.
- Robotic logging technology
- Nano biochips
- Nano 3D printing
- Nanorobotics in Gene Therapy
- Nanorobots in Cancer Detection and Treatment
- Nanorobotics in Surgery

Track 11: Nano-coatings
The term nanocoating alludes to nanoscale (i.e. with a thickness of a couple of tens to a couple of several nanometers) thin-films that are connected to surfaces all together make or enhance a material's functionalities, for example, erosion assurance, water and ice insurance, contact lessening, antifouling and antibacterial properties, self-cleaning, warmth and radiation opposition, and thermal administration. Nanocoating’s are Nano measured particles contained a type of mineral or compound that is normally painted onto a surface, for the most part being a machine or some likeness thereof, to help the gadget in a wide variety of capacities. Nanocoatings offer noteworthy advantages for applications in the protection, medicinal, aviation, oil and marine businesses, have driven makers to consolidate multi-useful coatings in their items.
- Anti-corrosion coatings
- Anti-abrasion coatings
- Antibacterial coatings
- Water proof and non-stick coatings
- Anti-reflection coating
- Thermal barrier coatings

Track 12: Nanobiotechnology
The term Nanobiotechnology refers to the combination of nanotechnology and biology. The concepts that are enhanced through nanobiology include: Nanoparticle, Nano device and Nano scale phenomena that occurs within the discipline of nanotechnology. This approach to biology allows scientists to imagine and create systems that can be used for biological research. Revolutionary opportunities and future scope of nanobiotechnology are gaining its utmost importance in nano life sciences.
Applications in pharmaceuticals and molecular diagnostics, include drug delivery, drug discovery and drug development. Nanobiotechnology has extending the limits of detection to single molecules by refining the current molecular diagnostics. Nanoparticles play a vital role in the delivery of biological treatments, which include gene therapy, RNA interference, cell therapy, vaccines, and antisense therapeutics. The most promising application of nanobiotechnology is for the development of customized drugs. The combination of diagnostics with therapeutics, refinement of molecular diagnostics, and targeted drug delivery play important roles in this application. At last, the safety issues of nanoparticles are discussed including measures to address these. The prospects of nanobiotechnology are incredible.
- Gene Therapy
- Cellular Engineering
- Nano systems
- Lipid Nanotechnology
- Therapeutic applications
- Bioluminescent magnetic nanoparticles
- Nano-Mechanisms for Molecular Systems
- DNA Nanotechnology
Track 13: Nanomedicine and drug delivery
Nanomedicine is the use of the nanotechnology (building of small machines) to the prevention and treatment of disease in the human body. Nanomedicine is a field of medical science whose applications are expanding increasingly on account of biological machines and nanorobots. Nanorobots are headways in nanomedicine as miniature surgeons. These machines help correct genetic deficiencies by replacing or altering DNA molecules, and repair damaged cells. For example, artificial white and red Blood cells, antiviral, artificial antibodies, and nanorobots. These nanomachines could influence the behaviour of individual cells.
Nanotechnology has given the likelihood of delivering drugs to targeted cells utilizing nanoparticles. The general drug intake and reactions might be brought down altogether by storing the dynamic agent in the morbid region only and in no higher measurement than required. Targeted drug delivery is proposed to lessen the side effects of drugs. Drug delivery centres around amplifying bioavailability both at particular places in the body and over some stretch of time. This can possibly be accomplished by molecular targeting by nanoengineered gadgets.
- Nanodrug delivery method
- Nanomedical devices
- Personalized nanomedicine
- Nanotechnology based imaging technologies for diagnosis and therapy
- Nanocapsules and nanocarriers
- Nanoparticles: Health effects and toxicity
- The future of nanomedicine
Track 14: Nanopharmaceuticals
Nanotechnology could be deliberately implemented in development of new drug delivery systems that can extend drug markets. Such a method would be applied to drugs selected for full-scale development based on their safety and efficacy information, but which fail to reach clinical development on account of poor bio pharmacological properties. The new drug delivery methods are required to enable pharmaceutical companies to reformulate existing drugs available, thereby expanding the lifetime of products and upgrading the performance of drugs by increasing effectiveness, safety and patient adherence, and finally lessening the healthcare costs.
Nanopharmaceutical refers to all aspects of nanotechnology-based pharmaceutics that applies to formulation, development and delivery aspects of pharmaceuticals. Nanomaterials (Nano size materials) that bring specific shapes and functionalities and nanodevices demonstrate a vital role in pharmaceutical nanotechnology. Nanopharmaceutics is the anticipation of healthcare and has gigantic promise.
- Nanoliposome
- Nanopharmaceuticals from the bench to Scale up
- Design of Nanopharmaceuticals
- Nano engineered drugs
- Nanosuspensions and nanoemulsions
- Biodegradability, Transformation, Alteration, Bioaccumulation
- Challenges and advances in Nanopharmaceuticals
Track 15: Cancer nanotechnology
Cancer Nanotechnology is associated with creating and using the develops of variable science and engineering with measurements at the nano-scale level equivalent to those of biomolecules or biological vesicles in the human body. It is the branch of nanotechnology concerned with the application of both the nanotechnology and nanomaterial ways to deal with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
- Nano materials for cancer diagnosis
- Nanotheranostics for Cancer
- RNA Nanotechnology for Cancer treatment
- Nano-enabled Immunotherapy
- Nanotherapy for Cancer
Track 16: Nano-biomaterials
Nanotechnology has made great advance forward really taking shape of new materials, new surfaces and new structures which additionally ï¬nd application in the biomedical ï¬eld. Prerequisite for the choice of the biomaterial is its adequacy by the human body. A biomaterial utilized as an implant should have some imperative properties keeping in mind the end goal to long haul usage in the body without notoriety. This session covers a broad scope of subjects identified with the preparing, portrayal, demonstrating, and uses of nanostructured therapeutic device materials and natural materials.
- Types of Nanostructured Biomaterials
- Processing and Characterization of Nanostructured Biomaterials
- Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering
- Biomaterials for bone repair and regeneration
- Polymeric Biomaterials
Track 17: Nanotechnology safety and risks
In spite of the fact that the Infinite potential of nanotechnology is empowering the risks of nanoparticles have not been completely perceived. The broad condition of nanoparticles isn't a danger; however, it is basic to measure the opportunities and risks of nanotechnology in products and applications that may influence the earth. As particles are getting smaller in measure, the more receptive they will be. According to increased reactivity, the impacts of a substance is unsafe. Henceforth nanotechnology can make ordinarily harmless substances accept risky qualities. Nanoparticles' large relative surface territory likewise empowers them to apply a more grounded impact on their condition and to react with different substances. Nanotechnology supporters trust that it can possibly change our lives drastically, while opponents of nanotechnology expect that self-recreating "nanobots" could escape from research facilities and lessen all life on earth. Some moral discussions have been centered around the field of molecular nanotechnology. The absence of worthy morals look into proposition might be identified with the trouble in recognizing or envisioning moral issues that are special to nanobiotechnology, especially its close term applications.
- Risk Assessment and Management
- Health Impact of Nanotechnology
- Societal Impact of Nanotechnology
- Environmental Impact of Nanotechnology
- Regulation of Nanotechnology

Track 18: Future of nanotech and nanobiotechnology
Certain highlights of nanotechnology have been observed that are probably going to be important in determining its impact in the future. All the more essentially, reacting to the test of nanotechnology will require going up against "philosophical" inquiries regarding the kind of society we wish to make and the part that innovation may play in making it. Nanotechnology is rapidly picking up traction over a scope of industries, from energy storage to agriculture to water treatment. Today, nanotechnology is a standout amongst innovative, cutting-edge areas of scientific study and it keeps on progressing at amazing rates. From researchers at technology-centered companies and institutions to students pursuing a nanotechnology degree, pioneers in nanotechnology are making the latest breakthroughs in the field.
- In Healthcare Sector: Drug Delivery
- Agriculture: Crop Protection and Livestock Productivity
- Water Treatment: Safe Purification
- Diseases: Early Detection
- Energy Storage: Solar Power
- Nanoparticle-Filled Ink Conducts Electricity

Learn More
Nanotechnology Universities in USA:
College of Nanoscale Science and Engineering | Johns Hopkins University | Virginia Commonwealth University | University of Central Florida | University of California, Berkeley | Northeastern University | University of California, Irvine | University of Tennessee | Northwestern Polytechnic University | George Mason University | University of New Mexico | Northwest Missouri State University | Saint Francis University | Millersville University | University of Maryland | Virginia Tech | Penn State York | Stony Brook University | California University of Pennsylvania | North Dakota State College of Science | University of Wisconsin-Stout | North Dakota State University | Mansfield University of Pennsylvania | University of California, Los Angeles | Wayne State University | University of Utah | Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey | Stevens Institute of Technology | University of Denver | University of Central Florida, Shore light | Louisiana Tech University | University of Connecticut | University of Colorado Boulder | University of North Carolina at Greensboro | Arizona State University | Johns Hopkins University | University at Albany, The State University of New York | University of Oklahoma | University of Washington | University of Maryland, College Park | University of Pittsburgh
Nanotechnology Universities in Europe:
Bangor University | University of Birmingham | University of Bristol | Cranfield University | University of Glasgow | Lancester University | University of Strathclyde | University of Surrey | Swansea University | Teesside University | Aalto University | Aarhus University | Barcelona University | University of Cambridge | Chalmers University of Technology | University College Dublin | University of Erlangen-Nurnberg | University of Greenwich | Grenoble Institute of Technology | Imperial College London | Linkoping University | National University of Ireland, Galway | National University of Science and Technology (MISIS) | University of Oxford | Politecnico de Torino | Politecnico de Milano | Queen’s University Belfast | Rovira I Virgili University | University College London (UCL) | University of Southampton | Technical University of Denmark | University of Twente | Ulster University | University of Valencia
Nanotechnology Universities in Asia and Middle East:
VIT University, India | Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore | IITs | NITs | Nano Science and Technology Consortium, Delhi | Hong Kong University of Science and Technology | Preston Institute Of Nanoscience And Technology (PINSAT), Islamabad | National University of Singapore (NUS) | Center of Excellence in Nanotechnology at AIT | College of Nanotechnology at KMITL | University Putra Malaysia | Sri Lanka Institute of Nanotechnology (SLINTEC) | The University of Tokyo | Tokyo Institute of Technology | Indian Institute of Nano Science & Technology Bangalore
Nanotechnology and Nanobiotechnology Societies in USA:
International Institute for Nanotechnology (IIN) | American Nano Society | International Association of Nanotechnology (IANT) | IEEE Nanotechnology Council | Institute for Molecular Manufacturing (IMM) | Microscopy Society of America (MSA) | Nano Science and Technology Institute (NSTI) | NanoBusiness Alliance | American Chemistry Council Nanotechnology Panel | International Council on Nanotechnology (ICON)
Nanotechnology and Nanobiotechnology Societies in Europe:
European Society for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology (EUSPEN) | British Society for Nanomedicine | Nanotechnology Industries Association (NIA) | Royal Microscopical Society | Royal Society - Nanotechnology and Nanoscience | Institute of Nanotechnology | Schau-Platz NANO | Safenano | Innovationsallianz Carbon Nanotubes (Inno.CNT) | Czech Nanotechnology Industries Association | European Society for Molecular Imaging (ESMI) | Erwin Schrödinger Society for Nanosciences | National Institute for Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology and Nanobiotechnology Societies in Asia and Middle East:
Nano Technology Research Association | Russian Society of Scanning Probe Microscopy and Nanotechnologies | Nano Science and Technology Consortium (NSTC) | Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences | National Centre for Nano-Structured Materials, CSIR | Institute of Nano Science and Technology | Iran Nanotechnology Initiative Council (INIC) | Sri Lanka Institute of Nanotechnology | National Nanotechnology Center (NanoTec) | National Center for Nanoscience and Technology
Nanotechnology Journals
Nano Letters | Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (JNN) | Nanotechnology | Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology | NanoTrends | Journal of Nanophotonics (JNP) | ACS Applied Nano Materials | ACS Nano | Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology| American Journal of Nanomaterials | Applied Nanoscience | Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine and Biotechnology | Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology | Bioinspired, Biomimetic and Nanobiomaterials | Biomedical Microdevices: bioMEMS and Biomedical Nanotechnology | BioNanoScience | Cancer Nanotechnology | Current Nanoscience | Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures | e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology | Environmental Science: Nano | European Journal of Nanomedicine (EJNM) | Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures | Hans Journal of Nanotechnology | HSOA Journal of Nanotechnology: Nanomedicine & Nanobiotechnology | IEEE Nanotechnology Magazine | International Journal of Biomedical Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (IJBNN) | International Journal of Green Nanotechnology | International Journal of Nano and Biomaterials (IJNBM) | International Journal of Nano Device, Sensor and Systems (IJ-Nano) | International Journal of Nano Dimension (IJND) | International Journal of Nano Studies & Technology | International Journal of Nanoelectronics and Materials (IJNeaM) | International Journal of Nanomanufacturing (IJNM) | International Journal of Nanomedicine | International Journal of Nanoparticles (IJNP) | International Journal of Nanoscience | International Journal of Nanotechnology | International Journal of Nanotechnology and Applications (IJNA) | International Journal of Smart and Nano Materials | International Nano Letters | ISRN Nanotechnology | Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology | Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology (JBN) | Journal of Bionanoscience | Journal of Experimental Nanoscience | Journal of Geoethical Nanotechnology | Journal of Micro - Nano Mechatronics | Journal of Nano Education | Journal of Nano Research (JNanoR) | Journal of Nano- and Electronic Physics | Journal of Nanobiotechnology | Journal of Nanoelectronics and Optoelectronics (JNO) | Journal of Nanoengineering and Nanosystems | Journal of Nanomaterials | Journal of Nanomaterials & Molecular Nanotechnology (JNMN) | Journal of Nanomechanics and Micromechanics | Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology (JNMNT) | Journal of Nanoneuroscience | Journal of Nanoparticle Research | Journal of Nanostructured Polymers and Nanocomposites (JNPN) | Microfluidics and Nanofluidics | NANO | Nano Biomedicine and Engineering | Nano Hybrids and Composites | Nano LIFE | Nanobiomedicine | Nanomaterials | Nanoscale | Nanotoday | Nanotoxicology | Nature Nanotechnology | World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering